The Trimontium Museum in Melrose, located in the Scottish Borders, is an important center for Roman history and archaeology. It stands out not only for its extensive collection but also for its innovative use of Virtual Reality technology in museums.
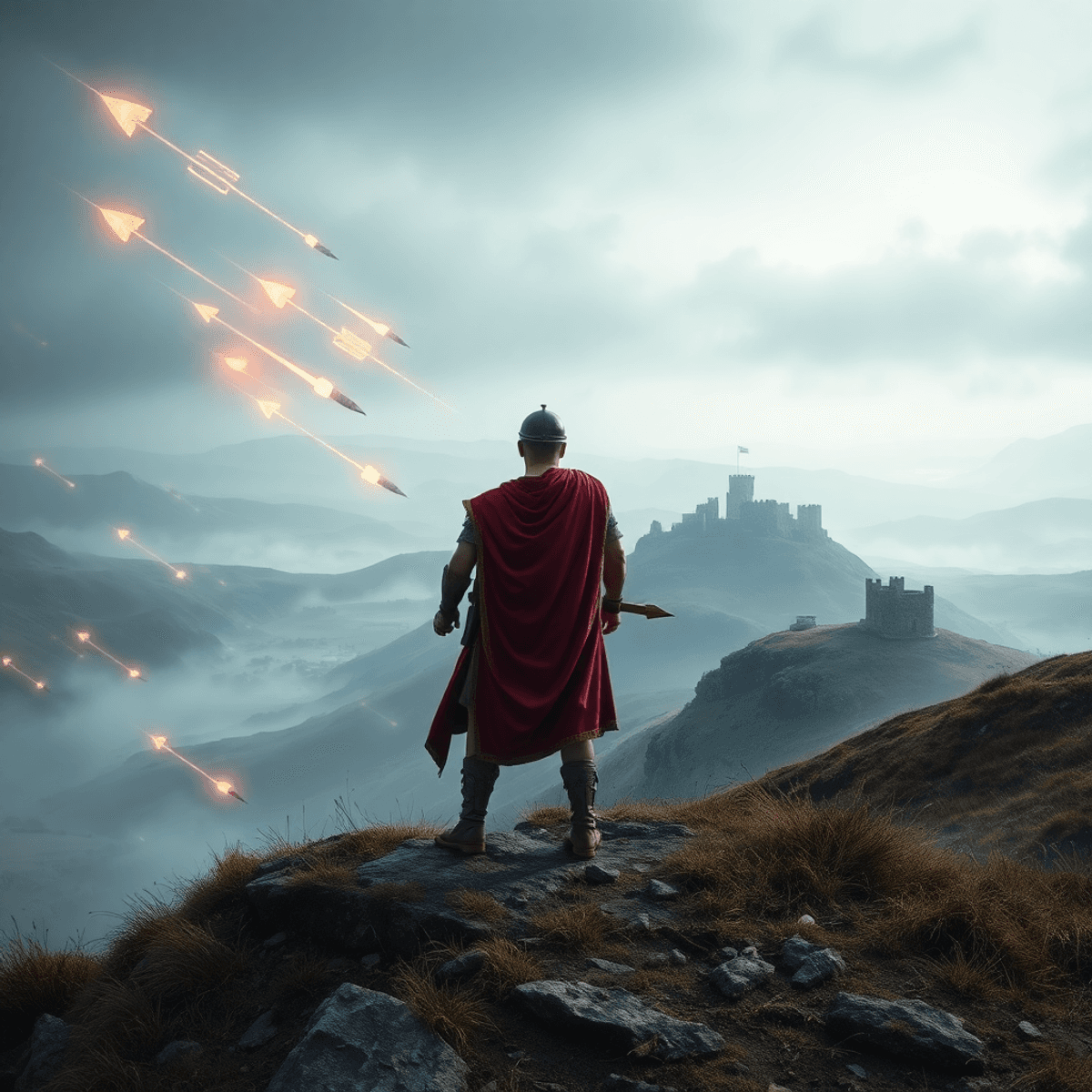
This cutting-edge approach vividly evokes a Roman assault on a hillfort community, transporting visitors back to an Iron Age battlefield with immersive detail. The VR experience at Trimontium Museum allows you to witness an ancient world brought to life like never before.
In this article, you will explore:
These elements combine to create a unique perspective on Roman military campaigns and their effects on local communities in the Scottish Borders.
Trimontium is one of the largest Roman forts in Scotland, strategically located beyond Hadrian’s Wall. This position shows the Romans’ ambitious efforts to expand into northern Britain during their military campaigns. As a crucial outpost, Trimontium served as a base for Roman soldiers and a center for overseeing local populations and movements across the Scottish Borders.
The Scottish Borders region is known for its high number of Iron Age hillforts, which were important defensive settlements even before the Romans arrived. Among these, Burnswark Hill stands out as an archaeologically significant site. Excavations over the years have revealed large amounts of projectile remains, particularly sling bullets and ballista balls. These discoveries indicate substantial military activity around the hillfort.
Archaeologists and historians continue to discuss what these artifacts mean:
Roman military operations in northern Britain sought to suppress local resistance and expand imperial control. The existence of well-fortified hillforts suggests that local tribes actively defended their lands against Roman encroachments. The archaeological findings from Burnswark Hill vividly capture this confrontation, providing concrete evidence of the struggle between an imperial power and indigenous communities.
Understanding the significance of Trimontium alongside Burnswark Hill enhances your understanding of how Roman forces functioned far beyond their usual frontier defenses.
Virtual Reality technology in museums offers a powerful tool for bringing history to life, and the Trimontium Museum employs this immersive technology for history exploration with impressive effect. At the heart of the museum’s VR experience is a meticulously digital reconstruction of the Roman assault on Burnswark Hill. This reconstruction captures the landscape, fortifications, and thousands of figures with remarkable detail and accuracy. Visitors are transported back nearly two millennia, standing virtually among warriors and Roman soldiers as the assault unfolds.
Key contributors to this project include:
This collaboration bridges archaeology and digital technology seamlessly.
The educational benefits of using VR in this context are significant:
VR transcends the limits of static displays by allowing visitors to explore scale, strategy, and human stories embedded within archaeological data. It transforms fragments like sling bullets and ballista balls into vivid narratives that illuminate the realities behind ancient conflicts. This approach makes deep historical knowledge accessible without sacrificing scholarly rigor or authenticity.
The Trimontium Museum in Melrose is using Virtual Reality technology to vividly evoke a Roman assault on a hillfort community, creating an experience that balances educational depth with emotional sensitivity. Designed for children aged 8 and above, this historical VR experience handles intense themes thoughtfully without resorting to graphic violence. This approach makes it accessible for younger audiences while respecting the gravity of the events portrayed.
Visitors are transported into immersive vignettes that humanize both defenders and attackers. The VR session captures moments of fear, hope, and final farewells among the Iron Age hillfort inhabitants under siege. For example:
These carefully crafted scenes draw visitors beyond mere observation toward empathy with individuals caught in historical conflict. The emotional resonance is enhanced by narration that invites reflection on the human cost of war, connecting ancient events to modern experiences of conflict and displacement.
Experiencing Roman history through virtual reality experiences like this allows you to engage with archaeological data in a deeply personal way. Rather than reading facts or viewing static exhibits, you feel the tension and uncertainty faced by those living at Burnswark Hill over 2,000 years ago. This emotional engagement strengthens understanding and retention of historical knowledge, making it a powerful tool for education.
Key benefits include:
These elements combine to make the Trimontium Museum’s VR sessions not only informative but profoundly moving encounters with Scotland’s Roman past.
Visitors to the Trimontium Museum can explore the VR experience alongside the museum’s rich exhibitions and galleries. The museum is open 7 days a week from 10am to 4:30pm, providing ample opportunity to plan a visit.
The virtual reality sessions run four times daily, accommodating a steady flow of guests eager to immerse themselves in the Roman assault on Burnswark Hill. Due to limited availability, pre-booking is strongly recommended to secure your place in a session. This ensures you won’t miss out on this unique interactive experience.
Tickets for the VR session also grant access to the museum’s recently renovated main galleries. These galleries showcase an extensive collection of artefacts from both the Iron Age hillfort communities and the Roman fort occupants. The physical exhibits complement the VR experience by grounding visitors in tangible history—offering context and depth to what you see through the headset.
When planning your visit, check the museum’s official website for museum VR session booking information and updates on exhibitions. This helps you coordinate your time effectively between viewing artefacts and engaging with cutting-edge virtual reconstructions that bring ancient history vividly to life.
The Trimontium Trust sets a compelling example of how archaeology and digital technology can intersect to redefine museum education. Collaboration between archaeologists and digital historians, such as the partnership with Virtual Histories, plays a crucial role in ensuring that historical interpretations are both accurate and engaging. Archaeological evidence informs the digital reconstructions, while experts in virtual reality contribute technical skills and creative storytelling techniques. This synergy allows visitors to experience history not just as static displays but as living, immersive narratives.
Using VR technology offers significant benefits for heritage preservation:
Challenges arise in maintaining authenticity within digital reconstructions:
The impact on visitor engagement is unmistakably positive:
By combining traditional archaeological methods with cutting-edge technology, Trimontium Trust demonstrates a forward-thinking approach that enriches public understanding of the past while embracing the future of museum education.
The Trimontium Museum in Melrose is using Virtual Reality technology to vividly recreate a Roman attack on a hillfort community, giving you a rare opportunity to understand the historical context of Roman attacks on hillforts in northern Britain. This immersive experience goes beyond traditional exhibits, inviting you to think about:
By visiting the museum, you connect with history in a way that feels immediate and real. You see not only what the Romans brought—roads, forts, administration—but also what they imposed: conflict, displacement, and cultural disruption. This unique combination of archaeology and advanced technology encourages you to view history from different perspectives, enhancing your understanding of past lives shaped by empire and resistance.